Discover what the DISTINCT SQL clause is, what it does, and when to use it.
Preface
Many developers have heard about the DISTINCT SQL clause. Queries using such an SQL clause return distinct (i.e. unique) results and as such, queries employing the DISTINCT SQL modifier are very useful for developers, DBAs, and other kinds of engineers alike.
The Internals of the DISTINCT SQL Clause
So, how do queries utilizing the DISTINCT SQL clause work internally? It’s all quite simple:
- The
DISTINCTSQL clause is used together withSELECTqueries. - Once we ensure that the query we run is indeed a
SELECTquery, we utilize theDISTINCTSQL clause after theSELECTquery has been invoked:SELECT DISTINCT column FROM tableworks. - The
DISTINCTSQL clause should return unique (distinct) results from a table adhering to the filter in ourSELECTquery.
The DISTINCT SQL clause can also be mixed together with the LIMIT SQL clause to return the first X results like so (here we return the first 50 results because of LIMIT 50):
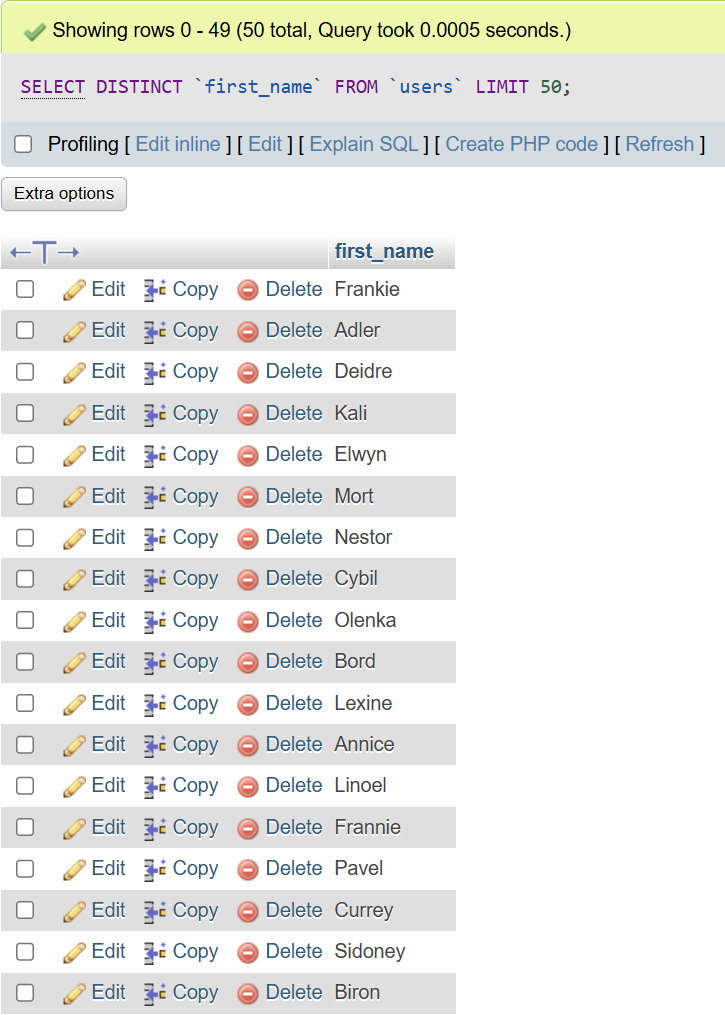
We’ve returned distinct (unique) first names of users in the users table. Woohoo!
Because of the nature of this SQL clause, SQL queries using DISTINCT can be used to retrieve unique values from a single column, find unique combinations of rows in multiple columns if multiple columns are specified after the SQL DISTINCT clause, count unique entries in a table, identify the unique rows of data in a table for data analysis, delete duplicate rows in a table, or perform a set of other actions.
Beyond the DISTINCT SQL Clause in Databases
With that being said, both developers and database administrators have many other things to worry about besides the clause! Data performance and security is always of paramount importance, and to ensure the security of your most precious data, ensure you use data breach search engines like BreachDirectory.com as data breach search engines like BreachDirectory.com will help you see if your data has been stolen in any data breach while also helping you perform a wide variety of investigative activities on email addresses, usernames, Blockchain or IP addresses, or other data classes:
Give BreachDirectory.com a spin today, and until next time!
Summary
The SQL DISTINCT clause is used to remove duplicate rows from a data set and it can be used within any SELECT query in any relational database management system.
Besides this SQL clause, database management systems and applications have many other things you should care about. You should care about the performance and security of your applications and databases as well because if you don’t, data is likely to get stolen, and once it gets stolen, end up in the hands of cybercriminals (or, if you’re lucky, data breach search engines like BreachDirectory.)
Keep your data and databases safe, and until next time!
FAQ
What is the SQL DISTINCT Clause?
Queries built upon the SQL DISTINCT clause return distinct (i.e. unique) rows based on a SELECT query. The SELECT query in question can have modifiers (WHERE, LIMIT, etc.)
Can You Use COUNT DISTINCT SQL Too?
Yes, you can use COUNT DISTINCT SQL clauses together with the DISTINCT clause in an SQL statement. An SQL statement that would use these clauses would look like so:
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT column) FROM table;
Why Should I Use BreachDirectory.com?
Consider using data breach search engines like BreachDirectory.com because such data breach search engines will help you see if your data has been stolen in any data breach while also helping you perform a wide variety of investigative activities on email addresses, usernames, Blockchain or IP addresses, or other data classes.
